
What Are Magnesium Gummies Good For?
Up to 75% of adults fail to meet their daily magnesium needs? If you’ve ever tossed and turned at night, battled midday brain fog, or woken up to muscle cramps, low magnesium could be the culprit.
Enter magnesium gummies: a tasty, hassle-free way to top up this essential mineral. While there are plenty of magnesium supplements to choose from, magnesium gummies are growing in popularity due to their ease of use and natural flavours.
In this guide, we’ll explore what magnesium gummies are good for—think better sleep, steadier moods, and stronger muscles—and show you how easy it is to make them part of your daily routine.
What is magnesium?
Magnesium is a mineral that ensures the body functions properly. Despite its presence in many foods, including nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables, it's unfortunately one of the most common deficiencies in the UK.
Magnesium plays an essential part in over 300 biochemical reactions, including:
- Promoting nerve and muscle function
- Energy production
- Regulating heart rhythm
- Bone health and strength
- DNA creation
- Protein synthesis
- Blood sugar regulation
The types of magnesium:
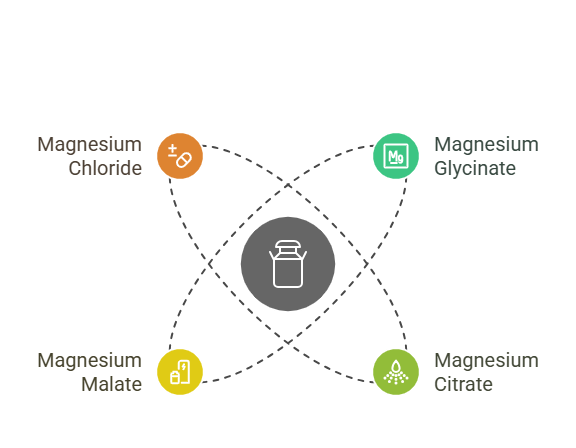
- Magnesium Glycinate: This form of magnesium is bound to an amino acid that boasts calming properties, making it ideal for muscle relaxation, stress, sleep, and anxiety.
- Magnesium Citrate: Magnesium citrate (citric acid) is one of the best forms of magnesium, thanks to its high bioavailability. It offers a variety of functions, including improving muscle function, supporting bone health, and easing constipation—thanks to its water-absorbing effects.
- Magnesium Malate: Paired with malic acid, this form of magnesium boosts energy production - but it can also treat muscle pain and fatigue.
- Magnesium Chloride: This form of magnesium is incredibly versatile. It's often used in heartburn treatments and is a popular topical solution.
While these are the most common forms of magnesium, other options are also available, including magnesium sulfate and magnesium oxide.
Who is most at risk of developing a magnesium deficiency?
Anyone who doesn't get enough magnesium from diet alone is at risk of a deficiency, but some groups are more vulnerable than others. These include:
- Gastrointestinal Conditions: People with inflammatory bowel conditions, such as celiac and Crohn's disease.
- Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes has a range of side effects, including increased magnesium loss when urinating.
- Older Adults: Seniors often find that their magnesium absorption rate decreases with age, but deficiencies can occur due to dietary changes.
- Lifestyle Choices: People who consume an unhealthy diet won't get enough magnesium, but heavy drinkers experience higher levels of excretion.
- Medications: Certain medications, including PPIs (proton pump inhibitors), antibiotics, and chemotherapy, can speed up magnesium loss.
The risks associated with magnesium deficiency
According to Edge Hill University, research suggests that 10% to 30% of individuals in developed countries may have a magnesium deficiency.
These deficiencies can range from mild to severe, but the important thing to remember is that even mildly low amounts of the mineral can have a detrimental impact on your overall health, including:
- Neuromuscular Problems: Magnesium can impact your muscles, leading to leg cramps - most common during the evening. Some people also notice tingling, numbness in their lower extremities, and general weakness. In the most severe cases, seizures and convulsions may also occur.
- Heart Problems: Magnesium maintains the heart's electrical stability, with deficiencies often leading to palpitations and irregular heartbeats. There's also a risk of developing high blood pressure and artery spasms.
- Bone Health: Magnesium's ability to regulate Vitamin D and calcium levels means low levels of it can increase the risks of developing osteoarthritis and other complications.
- Mental & Neurological Health: Many people believe that magnesium can calm nervous symptoms, which in turn regulate moods. Individuals with low levels might also experience frequent migraines.
- Metabolic Disorders: Magnesium deficiencies can result in insulin resistance, increasing the chances of developing Type 2 diabetes.
The many health benefits of magnesium supplements

Magnesium offers an array of health benefits as an essential mineral - but what happens if you don't get enough of it? Magnesium supplementation is one of the best ways to increase your levels and fill any nutritional gaps.
While supplements shouldn't replace a balanced diet, they still offer plenty of benefits.
Less anxiety and stress
Magnesium regulates the nervous system and stabilises natural stress responses, leading to less anxiety and depression. Studies show that the mineral can reduce symptoms of depression, making it a beneficial supplement for mental health (NIH).
While magnesium gummies can be beneficial for your daily intake, it's important to remember that severe depression symptoms may require antidepressants, so you should use magnesium as an add-on treatment instead.
Sleep quality
High stress levels, hectic schedules, and general lifestyle factors can interrupt sleep schedules, leading to insomnia and disrupted circadian rhythms. Magnesium works by activating the parasympathetic nervous system, improving sleep quality and enhancing relaxation.
It also regulates your sleep/wake cycle by stabilising melatonin production. Numerous studies show that magnesium can support sleep quality by promoting relaxation in the evening and preventing daytime lethargy (ScienceDirect).
Cardiovascular support
People who consume magnesium-rich foods are less likely to develop low blood pressure, reducing their risk of heart disease.
If you don't get enough nutrients through diet alone, taking a magnesium supplement can reduce your blood pressure and protect you against cardiovascular disease. Research shows that people with a high magnesium intake are less likely to develop CVD (NIH).
Supporting muscular health
Athletes and people who work out frequently increase their magnesium intake, as it supports post-exercise recovery and can prevent muscle cramps or spasms.
A study from the Journal of Translational Medicine also concluded that people who take magnesium regularly typically recover from workouts quicker, suffer less muscle pain, and lower the risks of muscle damage.
Increasing bone density
Magnesium is essential for bones, which store around 60% of it. When you don't have enough magnesium, your body's ability to metabolise calcium and absorb Vitamin D is affected, increasing the risks of developing osteoporosis.
While more research is required, one study showed promising results that magnesium can reduce the risks of fractures (PubMed).
Constipation relief
Some types of magnesium are renowned for their ability to relieve constipation. If you experience constipation regularly, taking either magnesium oxide or citrate can extract water from the intestines and soften stools, encouraging regular bowel movements.
However, you should always follow the dosage instructions when using magnesium gummies for constipation. Taking too much magnesium can have the opposite effect.
Blood sugar regulation
Last but not least, magnesium can reduce the risks of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The gummies won't automatically cure diabetes, but they do maintain healthy blood sugar levels and can reduce symptoms.
Stronger immune system
Magnesium is responsible for multiple reactions in the body and plays a key role in supporting the immune system. People with low magnesium levels may experience lower recovery from illnesses and be more susceptible to infections.
Individuals with a higher magnesium intake are less likely to experience immunity fluctuations, reducing their chances of a range of conditions, including chronic fatigue syndrome.
Magnesium recommended daily intake
When using magnesium supplements, it's important to follow the instructions carefully and never take more than recommended. However, if you suffer from a deficiency, you may need to take extra to ensure your body absorbs enough magnesium.
Here are the recommended daily intakes:
| Age | Female | Male |
| Up to 6 months old | 30mg | 30mg |
| Up to 12 months old | 75mg | 75mg |
| 1 to 3 years old | 80mg | 80mg |
| 4-8 years old | 130mg | 130mg |
| 9 to 13 years old | 240mg | 240mg |
| 14 to 18 years old | 360mg | 410mg |
| 19 to 30 years old | 310mg | 400mg |
| 31 and over | 320mg | 420mg |
Lactating women should increase their magnesium intake based on recommendations from their healthcare provider.
Sealions Magnesium Gummies
Magnesium gummies are an effective way to treat deficiencies and ensure you get enough nutrients when a balanced diet alone doesn't do the trick. Unlike many other magnesium supplements, our Magnesium Gummies are easy to take and have natural flavourings.
Instead of having to swallow pills, you can enjoy absolute convenience while giving your body a healthy boost of nutrients.
Each Sealions Magnesium gummy comes with a delicious natural strawberry flavour and 150mg of magnesium citrate, a more bioavailable version of the mineral. We also added 1.6mg of Vitamin B6 for neurological, immune system, and metabolic support.
Recommended Dosage:
Please take two 150mg Magnesium Gummies daily, equating to 300mg. It's essential to avoid exceeding this dose unless a healthcare provider advises increasing your intake.
Why buy Sealions Magnesium Gummies?
At Sealions, we're passionate about health and wellbeing. Our experts go out of their way to provide effective and affordable magnesium supplements using high-quality ingredients. So, how can we offer such low prices?
It's simple: we reduce our profit margins and pass the savings directly to you. Our customers get to stock up on supplements, save money, and enjoy convenient UK delivery.
Shop today, and please feel free to contact us with any questions.
FAQs
Are magnesium gummies effective?
Yes, as long as you buy a high-quality supplement. Magnesium, combined with a balanced diet and plenty of exercise, can enhance overall health and ensure your body gets optimal nutrients.
When should I take magnesium gummies?
It depends on why you're taking them. If you're taking them for your overall health, there's no issue with using them in the morning or at lunch. However, taking the gummies during the evening might be best if you're using them to enhance sleep quality.
Can I take the gummies daily?
Yes, as long as you understand the maximum daily limit and don't exceed it - unless you have a deficiency.
Are there any side effects associated with magnesium gummies?
You may experience some minor side effects, such as digestive issues and bloating - but this is usually only when you take too much.
How long until I feel the effects?
It depends on how your body responds to magnesium, but some people can notice fewer muscle cramps and better sleep quality within a few days. Others might find that it takes longer for their symptoms to improve.
Tagged:









